Involute gear

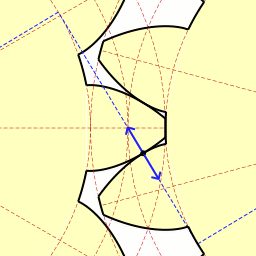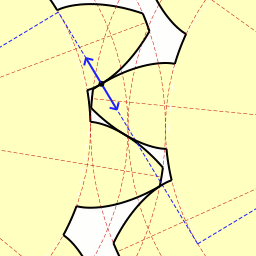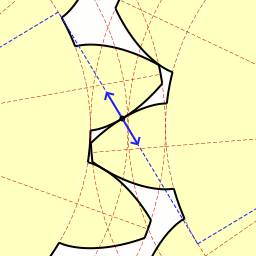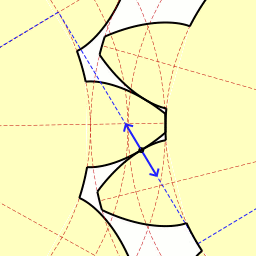

The involute gear profile is the most commonly used system for gearing today, with cycloid gearing still used for some specialties such as clocks. In an involute gear, the profiles of the teeth are involutes of a circle. The involute of a circle is the spiraling curve traced by the end of an imaginary taut string unwinding itself from that stationary circle called the base circle, or (equivalently) a triangle wave projected on the circumference of a circle.
Advantages and design
[edit]The involute gear profile, sometimes credited to Leonhard Euler,[1] was a fundamental advance in machine design, since unlike with other gear systems, the tooth profile of an involute gear depends only on the number of teeth on the gear, pressure angle, and pitch. That is, a gear's profile does not depend on the gear it mates with. Thus, n and m tooth involute spur gears with a given pressure angle and pitch will mate correctly, independently of n and m. This dramatically reduces the number of shapes of gears that need to be manufactured and kept in inventory.
In involute gear design, contact between a pair of gear teeth occurs at a single instantaneous point (see figure at right) where two involutes of the same spiral hand meet. Contact on the other side of the teeth is where both involutes are of the other spiral hand. Rotation of the gears causes the location of this contact point to move across the respective tooth surfaces. The tangent at any point of the curve is perpendicular to the generating line irrespective of the mounting distance of the gears. Thus the line of the force follows the generating line, and is thus tangent to the two base circles, and is known as the line of action (also called pressure line or line of contact). When this is true, the gears obey the fundamental law of gearing:[2]
The angular velocity ratio between two gears of a gearset must remain constant throughout the mesh.
This property is required for smooth transmission of power with minimal speed or torque variations as pairs of teeth go into or come out of mesh, but is not required for low-speed gearing.
Line of action and contact
[edit]The point where the line of action crosses the line between the two centres is called the pitch point of the gears. The sliding contact friction is zero at this point.
The distance actually covered on the line of action is then called line of contact. The line of contact begins at the intersection between the line of action and the addendum circle of the driven gear and ends at the intersection between the line of action and the addendum circle of the driving gear.[3]
The pressure angle is the acute angle between the line of action and a normal to the line connecting the gear centers. The pressure angle of the gear varies according to the position on the involute shape, but pairs of gears must have the same pressure angle in order for the teeth to mesh properly, so specific portions of the involute must be matched.
Pressure angle
[edit]While any pressure angle can be manufactured, the most common stock gears have a 20° pressure angle, with 14½° and 25° pressure angle gears being much less common.[4] Increasing the pressure angle increases the width of the base of the gear tooth, leading to greater strength and load carrying capacity. Decreasing the pressure angle provides lower backlash, smoother operation and less sensitivity to manufacturing errors.[5]
Types of involute gears
[edit]Most common stock gears are spur gears with straight teeth. Most gears used in higher-strength applications are helical involute gears where the spirals of the teeth are of different handedness, and the gears rotate in opposite directions. Studies have also been performed on gears having teeth with a non-involute curve profile.[6][7][8]
Helical involute gears are typically only used in limited situations where the spirals of the teeth are of the same handedness, the spirals of the two involutes are of different handedness, and the line of action is the external tangents to the base circles (analogous to a normal belt drive, whereas normal gears are analogous to a crossed-belt drive), and the gears rotate in the same direction,[9] such as can be used in limited-slip differentials [clarification needed][10][11] because of their low efficiencies, and in locking differentials when the efficiencies are less than zero.
References
[edit]- ^ "MOZIMTEC". www.mozimtec.de. Retrieved 2024-01-03.
- ^ Norton, R.L., 2006, Machine Design: An Integrated Approach, 3rd Ed, Pearson/Prentice-Hall, ISBN 0-13-148190-8
- ^ tec-science (2018-10-31). "Meshing of involute gears". tec-science. Retrieved 2019-10-22.
- ^ Juvinall, R.C. and K.M. Marshek, 2006, Fundamentals of Machine Component Design, 4th Ed, Wiley, ISBN 978-0-471-66177-1, p. 598
- ^ Boston Gear Company, Open Gearing Catalog, http://bostongear.com/products/open-gearing/stock-gears/spur-gears/spur-gears
- ^ Liu, Lei; Meng, Fei; Ni, Jiale (2019-10-01). "A novel non-involute gear designed based on control of relative curvature". Mechanism and Machine Theory. 140: 144–158. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2019.05.022. ISSN 0094-114X.
- ^ "Non-Involute Gearing, Function and Manufacturing Compared to Established Gear Designs | Gear Technology Magazine". www.geartechnology.com. Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- ^ US5271289A, Jr, Meriwether L. Baxter, "Non-involute gear", issued 1993-12-21
- ^ Professor Jacques Maurel, "Paradoxical Gears", http://www.jacquesmaurel.com/gears
- ^ Jacques Mercier, Daniel Valentin US Patent 4831890
- ^ Arthur J. Fahy, Neil Gillies US Patent 5071395
